Spotting in Pregnancy
While spotting is a relative common occurrence in early pregnancy, it can nevertheless be concerning. According to The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, approximately 15-25 percent of women experience bleeding in early pregnancy.
Spotting in first trimester pregnancies, or the first 12 weeks, is typically lighter in color than what one would experience with a regular menstrual flow. The color may also vary from a pinkish hue to red or even brown.
Although it is easy to be worried when experiencing spotting during pregnancy, it’s important not to panic. Most women who experience spotting during pregnancy continue on to have a completely healthy pregnancy and deliver a healthy baby.
How Common Is Bleeding During Pregnancy?
If you’re wondering how common is bleeding during pregnancy 6 weeks, you should rest assured that it is relatively common. In fact, spotting or light bleeding can occur anytime between one and two weeks after fertilization occurs. This happens when the fertilized egg becomes implanted in the lining of the uterus. At this time, the cervix may be more prone to bleeding as a result of more blood vessels being present. Implantation bleeding may last for a few days and typically occurs before a woman even realizes she’s pregnant.
In fact, this type of bleeding is sometimes mistaken for a regular period. There is no need to be worried about implantation bleeding. It should be kept in mind that any time bleeding or spotting occurs after a woman would have expected her period, it’s usually not implantation spotting, but is instead likely associated with early pregnancy instead.
Understanding the Difference Between Bleeding and Spotting During Pregnancy
In understanding whether to be concerned about spotting in first trimester pregnancies, it’s important to also understand the difference between actual bleeding and spotting. Vaginal bleeding that occurs during early pregnancy involves a discharge of blood that comes from the vagina. This type of bleeding can occur any time from the point of conception all the way through the end of the pregnancy.
Spotting is relatively common during the first three months. There is usually no need to be alarmed. This is particularly true if you only notice a few drops of blood. As long as there is not enough blood to fill an entire panty liner, there is no need to be worried.
By comparison, bleeding occurs when there is a much heavier blood flow. With actual bleeding, it will be necessary to wear a liner or even a pad in order to prevent blood from soaking through your clothing.
Regardless of whether you are spotting or bleeding, it is typically best to get in touch with your healthcare provider and then describe to him or her the symptoms you are experiencing.
Causes of Bleeding and Spotting During Pregnancy
It should be kept in mind that quite a few changes occur in the cervix during pregnancy. This is due to the high production of hormones that takes place during pregnancy. The presence of such hormones can cause the cervix to become softer.
In addition to bleeding at the time of implantation, there can be many other causes for spotting to occur during pregnancy. Among those causes is a cervical polyp, which is a growth on the cervix. During periods of high estrogen levels, such polyps are more likely to bleed. This is particularly true during an exam or sexual intercourse. Cervical polyps are completely harmless.
Other common causes of bleeding during early pregnancy include:
- Heavy lifting
- Sexual intercourse
- Excessive exercise
- Gynecological exams
In some cases, a vaginal infection can also lead to bleeding. When the cause of bleeding is a vaginal infection, it may also be accompanied by vaginal discharge.
Related: Heavy Implantation Bleeding: Pregnancy Or Period?
Loss of Pregnancy.
Certainly, no one ever wants to consider that bleeding might result in a loss of pregnancy, but miscarriage may also be a cause of bleeding that occurs during pregnancy. It’s certainly understandable that bleeding might trigger a concern regarding loss of pregnancy. According to a study; however, only 12 percent of the small number of women who experience bleeding in pregnancy actually had a loss of pregnancy. It should be noted that approximately two-thirds of women who do have a miscarriage experience bleeding. Given this; it’s important not to simply ignore bleeding during pregnancy.
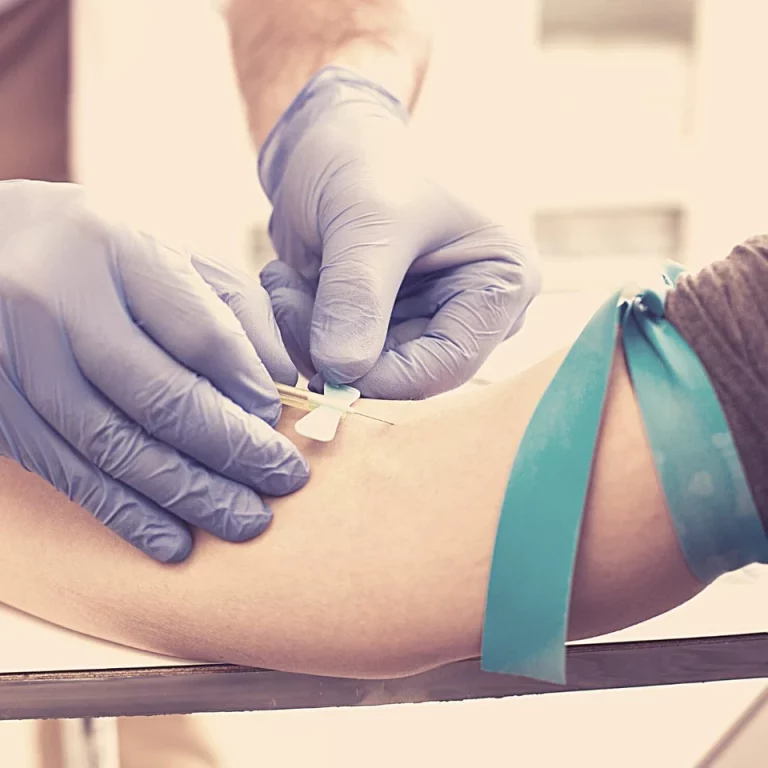
Diagnosis of Bleeding
A healthcare professional can perform tests to determine a possible cause of bleeding in pregnancy. For instance, an ultrasound can determine whether bleeding stems from pelvic organs, such as an ovarian cyst.
Blood tests may also be ordered to measure hCG, the pregnancy hormone. Low levels of this hormone might indicate that a pregnancy is not progressing properly. In some cases, progesterone levels may also be checked, as low levels of progesterone might result in bleeding or could indicate the presence of an abnormal pregnancy.
Bleeding in Pregnancy as a Result of Abnormal Pregnancies
When a pregnancy is not developing correctly, bleeding may be one of the first noticeable symptoms. For instance, if there is a genetic defect related to the embryo, bleeding could indicate an impending miscarriage. Once a miscarriage is in progress, it usually cannot be prevented.
Molar Pregnancies
Molar pregnancies, also sometimes referred to as gestational trophoblastic disease, refers to a pregnancy in which there is something abnormal about the fertilization. This results in abnormal tissue growing in the uterus. Although the pregnancy is not normal, a woman may experience the same symptoms associated with early pregnancy. Depending on the type of molar pregnancy that has occurred, there may or may not be a fetus present in the uterus. In some cases, there is only tissue and no fetus at all. In other cases, there may be an abnormally formed fetus. When this is the case, the fetus typically has severe birth defects. Molar pregnancies are not able to progress toward the delivery of a normal fetus. One of the early symptoms of a molar pregnancy is bleeding or vaginal spotting. Molar pregnancies are diagnosed with an ultrasound or sonogram.
Ectopic Pregnancies
When a fertilized egg does not implant in the uterus as it should, the result is an ectopic pregnancy. The egg may instead implant inside the Fallopian tubes. As the pregnancy progresses, there is a risk of the tube rupturing. Symptoms of an ectopic pregnancy may include vaginal bleeding and abdominal pain. A ruptured Fallopian tube can result in a significant amount of blood loss and could be potentially fatal. Emergency surgery and a blood transfusion may be necessary to resolve this life-threatening emergency.
When to See a Doctor
Anytime a pregnant woman experiences bleeding in pregnancy, it’s important to speak to a doctor. Although the bleeding or spotting could be completely harmless, it’s still important to determine the cause of the bleeding. While it’s quite likely that the cause of the bleeding is something relatively minor, other more serious causes of spotting or bleeding in pregnancy may include placental abruption, uterine rupture, placenta previa, or preterm labor. The best course of action is to see a healthcare professional as quickly as possible.
Managing Bleeding and Spotting in Pregnancy
In order to help manage spotting or bleeding in pregnancy and improve the chances of a healthy pregnancy continuing, a pregnant woman may be advised to stick to bed rest, stay well hydrated, spend time off her feet, limit physical activity, and elevate her feet.
We discuss products we think are useful to people. If you buy something through our links, we may earn a commission. Remember to check with your personal physician to see if a product recommended is right for you.