Why Do I Pee When I Sneeze Female: Stress Incontinence Of Urine
Experiencing an involuntary loss of urine while sneezing is a common issue faced by many women, often caused by stress incontinence. Stress incontinence occurs when the pelvic floor muscles, which support the bladder and control the release of urine, become weakened or damaged.
Understanding Stress Incontinence
Stress incontinence is a more common problem than you may think. Let’s take a look at why stress incontinence happens.
Anatomy of the Pelvic Floor
The pelvic floor is a group of muscles, ligaments, and tissues that support the pelvic organs, such as the bladder, uterus, and rectum. These muscles, also known as the pelvic floor muscles, play a crucial role in maintaining continence and preventing urine leakage. A strong and well-coordinated pelvic floor is essential for optimal functioning of the bladder and urethra, and their ability to control the release of urine.
Causes Of Urine Leakage During Sneezing
Stress incontinence occurs when the pelvic floor muscles are unable to withstand sudden increases in abdominal pressure, which can be caused by activities such as laughing, coughing, or sneezing. This type of incontinence is characterized by involuntary urine leakage and patients may notice drops of urine leaking out.
In women, stress incontinence can result from various factors, such as age, childbirth, weight gain, or a decline in estrogen levels during menopause (which can also result in overactive bladder during menopause). Pelvic floor muscle weakness can lead to a loss of bladder control and increased urine leakage.
Physical Factors Contributing to Stress Incontinence
There are several physical factors that can contribute to the development of stress incontinence in women. These include:
- Vaginal birth: Childbirth can weaken and stretch the muscles of the pelvic floor, which may lead to stress incontinence.
- Pelvic surgery: Certain surgical procedures, such as hysterectomy, can result in damage to or weakening of the pelvic floor muscles.
- Heavy lifting: Repeatedly lifting heavy objects can exert strain on the pelvic floor muscles, potentially leading to stress incontinence.
How Is Pelvic Organ Prolapse Related To Stress Incontinence?
Pelvic organ prolapse is not a cause of incontinence but often occurs alongside it. Unfortunately, fixing the prolapse does not necessarily fix the incontinence.
Risk Factors for Stress Incontinence
Several risk factors can increase a woman’s likelihood of developing stress incontinence. Some common risk factors include:
- Age: The risk of stress incontinence increases with age, as the muscles of the pelvic floor tend to weaken over time.
- Childbirth: Vaginal delivery can cause injury or weakening of the pelvic floor muscles, increasing the risk of incontinence.
- Weight gain: Excess body weight can increase abdominal pressure and strain the pelvic floor muscles.
- Pelvic surgery: Procedures that involve the pelvic floor or pelvic organs can increase the risk of developing stress incontinence.
Understanding stress incontinence and its contributing factors can help women seek appropriate treatments and strategies for managing this condition, thereby improving their quality of life.
Diagnosis Of Stress Incontinence
If you are a female who is peeing when they sneeze, then its important to have a proper evaluation. Here is what that looks like.
Consulting a Healthcare Provider
If you experience involuntary urine leakage when sneezing, it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider, typically a urologist or gynecologist. They will help identify the underlying medical condition and suggest appropriate treatment to improve your quality of life.
Medical History And Symptoms Review
During your appointment, your healthcare provider will review your medical history and discuss your symptoms in detail. It’s essential to share information about any medical conditions, previous surgeries, or urinary tract infections that may contribute to your situation. The provider will also evaluate other potential factors, such as pelvic floor disorders or issues with the nervous system, that could be causing the involuntary urine leakage.
Physical Examination Process
The provider will perform a physical exam to assess your condition further. This examination may include:
- Pelvic examination: The healthcare provider will examine your pelvic area to detect any abnormalities or signs of weakness in the pelvic floor muscles.
- Urine test: A urine sample will be collected to rule out urinary tract infections or other problems that may contribute to your symptoms.
- Cough stress test: During this test, you will be asked to cough forcefully while the provider observes for urine leakage. This test helps to confirm the presence of stress incontinence.
- Neurological examination: A brief assessment of your nervous system functioning may be conducted to identify any nerve-related issues that could cause involuntary urine leakage.
Once a thorough evaluation has been done, your doctor will be able to provide insight on why you are peeing when you sneeze. By identifying the issue, healthcare providers can develop an effective treatment plan to manage the problem and improve the patient’s quality of life.
Dealing With Stress Incontinence
There is a step wise approach to dealing with Stress Incontinence.
Support and Resources
First it is important to have access to care and support. Having access to support and resources can significantly improve the coping process for women experiencing SUI. Women dealing with SUI should consider discussing their condition with a health care provider, such as a women’s health expert. Health care providers can offer educational resources, recommend lifestyle changes, or suggest medical interventions.
In addition to professional care, seeking extra support from friends, family, or support groups can be helpful for women facing SUI-related challenges. Support groups provide a safe space to share experiences, coping strategies, and emotional hardships, fostering a sense of community and empowerment.
Behavioral And Lifestyle Changes
Making certain behavioral and lifestyle changes can significantly alleviate the symptoms of urinary incontinence when sneezing. These changes include:
- Adjusting fluid intake: Reducing or spacing out the consumption of fluids can help control the urge to urinate and minimize leakage.
- Bladder training: This involves increasing the time between bathroom visits and gradually helping the bladder hold more urine.
- Managing chronic coughing: Treating conditions like asthma or bronchitis that cause persistent coughing may ease stress incontinence.
- Refraining from smoking: Smoking can irritate the bladder and weaken the pelvic floor muscles.
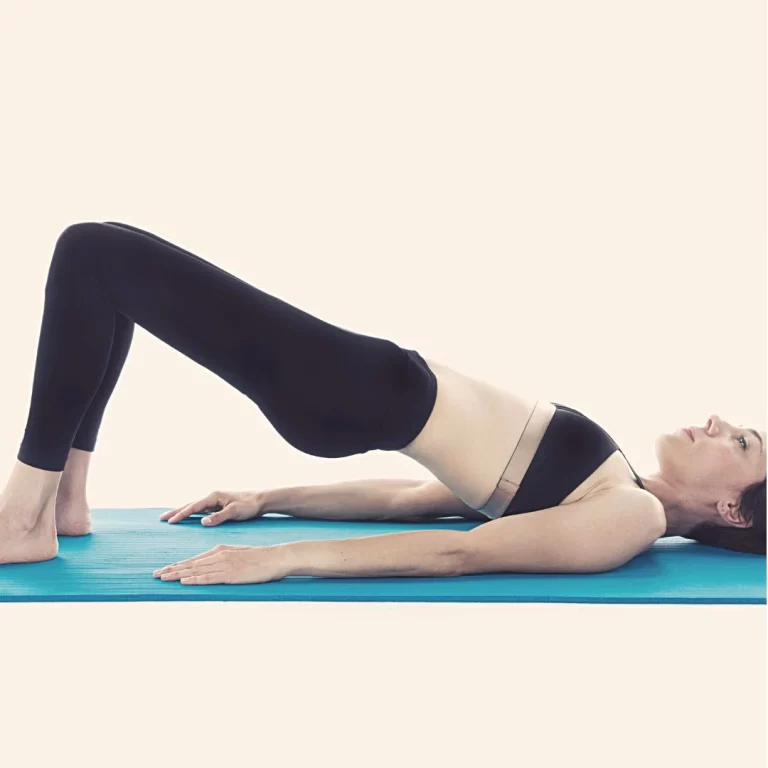
Pelvic Floor Exercises
Pelvic floor exercises, commonly known as Kegel exercises, are proven to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and improve control over urinary leakage. These exercises involve:
- Identifying the right muscles: The pelvic floor muscles can be located by stopping the urine flow midstream or tightening the muscles that prevent passing gas.
- Contracting and relaxing: Contract the pelvic floor muscles for 3-5 seconds and then relax them for an equal duration.
- Repeating the routine: Perform sets of 10 to 15 contractions, at least three times per day.
Physical Therapy and Expert Guidance
For those who struggle with pelvic floor exercises or need further assistance to manage their urinary symptoms, seeking help from a physical therapist specializing in pelvic floor therapy can be a helpful option. Physical therapists can provide:
- Personalized guidance on correct technique for performing pelvic floor exercises.
- Additional treatments, such as biofeedback or electrical stimulation, to enhance muscle control and awareness.
- Recommendations on other therapeutic interventions, like support devices, to better manage daily life with urinary incontinence.
Incorporating these strategies into daily routines can help women effectively manage the symptoms of urinary incontinence when sneezing and improve their overall quality of life.
Treatment Options For Treating Stress Incontinence
In this section, we will discuss various treatment options for women who experience urinary incontinence when sneezing. The treatments are categorized into non-surgical and surgical options.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Pelvic Floor Exercises
Also known as Kegel exercises, these exercises can help strengthen the muscles that control urine flow. They involve contracting and relaxing the muscles of the pelvic floor, assisting in preventing involuntary urine leakage.
Incontinence Devices
Devices such as pessaries can be inserted into the vagina to support the urethra and bladder neck, reducing the chance of urine leakage. A common example of an incontinence device is the vaginal pessary, which can be customized to fit the individual patient’s needs.
Lifestyle changes
Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding caffeine and alcohol, and practicing good bladder habits can help manage and reduce the severity of urinary incontinence.
Surgical Procedures And Treatment Options
Sling Procedure
A midurethral sling can be placed under the urethra for women suffering from stress incontinence. The procedure involves using a synthetic mesh or the patient’s own tissue to support the urethra and prevent urine leakage during activities that cause increased abdominal pressure, such as sneezing
Pelvic Surgery
In some cases, surgical procedures may be needed to correct any underlying anatomical issues that contribute to incontinence. This can include repairing or repositioning the bladder neck or urethra to provide better support and prevent urine leakage
Coping And Quality of Life
As you can imagine, having urine leak out when you are sneezing or coughing can be very frustrating.
Impact On Daily Activities
Stress urinary incontinence (SUI), which can cause involuntary urine loss during activities such as coughing or sneezing, can greatly affect a woman’s daily life and quality of life. Physical activities such as exercising or lifting heavy objects may also trigger SUI, potentially leading to a decrease in physical activity for some women.
Impact On Social Activities And Mood
The fear of embarrassment or inconvenience often impacts their social interactions, emotional wellbeing, and self-esteem.
Why Do I Pee When I Sneeze Female: Summary
Females who pee when they sneeze are likely suffering from stress incontinence. This can result from various factors such as pregnancy, childbirth, aging, or obesity. When pressure is applied to the bladder from actions like sneezing, coughing, or laughing, these weak muscles allow urine to leak. This is different from urge incontinence. Stress incontinence remains the most common type of urinary incontinence affecting women. This issue can significantly impact a woman’s quality of life. It is important to know that this is a common problem and that various treatment options are available to help manage and improve symptoms. In order to deal with this issue, females may adopt strategies such as wearing absorbent pads or protective undergarments, performing pelvic floor muscle exercises (Kegels) to strengthen the pelvic muscles, scheduling regular bathroom breaks to reduce the risk of accidents, and avoiding or reducing the consumption of bladder irritants (e.g., caffeine, alcohol, spicy foods).